What are the periodontal disease stages? What causes necrotizing periodontitis? What is the difference between a periapical and a periodontal abscess? Root canal treatment – the root can be retained by root canal treatment , which can also be used to drain the infection.
The presence of inflammation makes it tender when tapping or chewing on it.
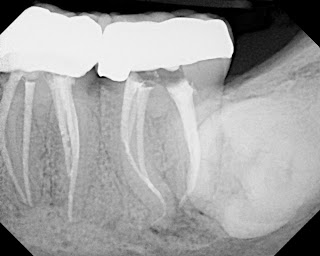
Note large restoration present in the tooth, which will have undergone pulpal necrosis at some point before the development of this lesion. Condition of periodontal and periapical tissues. As a rule, medical measures are painless, conducted under local anesthesia, and timely treatment to the dentist, makes treatment effective and fast.
Medication periodontitis is a conservative treatment , surgery is rarely used. Emergency Management of Acute Apical Periodontitis : A Systematic Review of the Literature Although toothache is a subjective symptom, it can have a significant social impact. Emergency dental treatment accounts for to of the costs of all dental therapy, an amount similar to all periodontal treatment costs.
Radiographically, there are diffuse radiopacities around the root apices. Non-surgical endodontic treatment is indicated followed by a build-up and crown.

Over time the condensing osteitis should regress partially or totally (15). Learn Facts About The Difference Between Gingivitis And Periodontitis. How To Prevent This Gum Disease. Find Your Toothpaste Today!
Acute periapical periodontitis is an inflammatory reaction of the periapical tissues of the tooth in response to an irritant stimulus in the dental pulp. The chosen treatment is usually endodontic therapy. It is usually caused by some sort of infection in the mouth, although trauma and and root canal treatment have also been known to cause the condition. There are two kinds of apical periodontitis , acute and chronic. Here is a case I treated that exhibited persistent symptoms and is similar in many respects to the one above.
The original symptoms and exam were indicative of irreversible pulpitis and extensive recurrent caries was located underneath the buccal margin. Acute Apical PeriodontitisAcute Apical Periodontitis Acute Inflammatory Periapical DiseasesAcute Inflammatory Periapical Diseases A common condition accompanied byA common condition accompanied by excruciating pain, a necrotic pulp, andexcruciating pain, a necrotic pulp, and radiographic thickening of the apicalradiographic thickening of the apical periodontal ligament space, treatmentperiodontal ligament space, treatment requires pulp extirpation or toothrequires pulp extirpation or tooth. In the early stages, periodontitis has very few symptoms, and in many individuals the disease has progressed significantly before they seek treatment.
Management involves the physical intervention of the process by a dentist under local analgesia. The treatment will either be to extract the tooth or to open the pulp chamber and root canal system, debride away necrotic debris, irrigate with an antiseptic and dressing with a combined steroid and antibiotic paste. If the irritation persists the inflammation becomes chronic.
Periodontitis periapicalis acuta purulenta clinical charasteristics: Is characterized by the presence of pus ,which may also lead to formation of abscess. In acute condition there is an increase in the submandibular lymph nodes, fatigue, fever and malaise.
An untimely treatment could lead to endodontic abscess. Chronic periapical periodontitis are slow progressing and long-term inflammatory reactions. They develop as complications of pulpitis, acute periapical periodontitis or injuries. The purulent form of periodontitis should be separated from the similar near-root cysts.
Acute apical periodontitis is differentiated with diffuse pulpitis, gangrenous pulpitis, exacerbation of chronic periodontitis , with acute osteomyelitis, periostitis. It is designed as a complementary step after standard root canal treatment. Objectives To evaluate the effects of systemic antibiotics provided with or without surgical intervention (such as extraction, incision and drainage of a swelling, or endodontic treatment ), with or without analgesics, for symptomatic apical periodontitis and acute apical abscess in adults.
Prevention or treatment of apical periodontitis.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.